
Business data is always on the move—patient records, financial statements, legal contracts. The way organizations handle that flow varies widely. Some have invested in modern, secure file exchange systems. Others still depend on outdated methods. That’s where problems arise. Even one lapse can disrupt operations, trust, and compliance.
Recognizing these stakes, businesses are shifting to secure, trackable file transfer processes. Organizations that adopt these solutions protect information while keeping teams aligned, maintain their reputation, and meet compliance requirements.
In this article, we break down the file transfer methods and virtual data room solutions to show you how they move sensitive data and turn secure file sharing into a business advantage.
Key takeaways
- Different tools fit different needs. SFTP, FTPS, HTTPS, and MFT all protect data. However, they vary in scalability, automation, and monitoring.
- Virtual data rooms centralize and simplify. Unlike other document exchange tools and file-sharing protocols, VDRs combine secure storage, access control, audit trails, and compliance features.
- Collaboration drives results. Teams and external partners work more efficiently when everyone accesses the same files in a controlled space. Real-time visibility reduces errors and accelerates decision-making.
- Security can be a strategic advantage. When data transfer works seamlessly, businesses gain confidence to scale, close deals faster, and pursue global opportunities without hesitation.
Why secure file transfer matters
The main risks of insecure document exchange include the following:
1. Data breaches
Breaches happen when files aren’t properly protected. Attackers can intercept, alter, or steal documents during transit. Globally, the average cost of a breach in 2025 dropped by 9%, to USD 4.44 million, partly because detection and containment are faster than before. But that doesn’t mean the problem is solved. One lapse can still cause big disruptions across an organization.
💡 Additional resources: How long does setting up a virtual data room take?
2. Regulatory penalties
The rules for moving data aren’t flexible. In particular, healthcare, finance, and government organizations face high stakes if they fail to comply. Take Anthem, for example—they paid a record $16 million HIPAA settlement in 2018 after breaches exposed the electronic protected health information of nearly 79 million people. That kind of outcome shows how quickly mistakes can turn into serious penalties.
3. Loss of client or partner trust
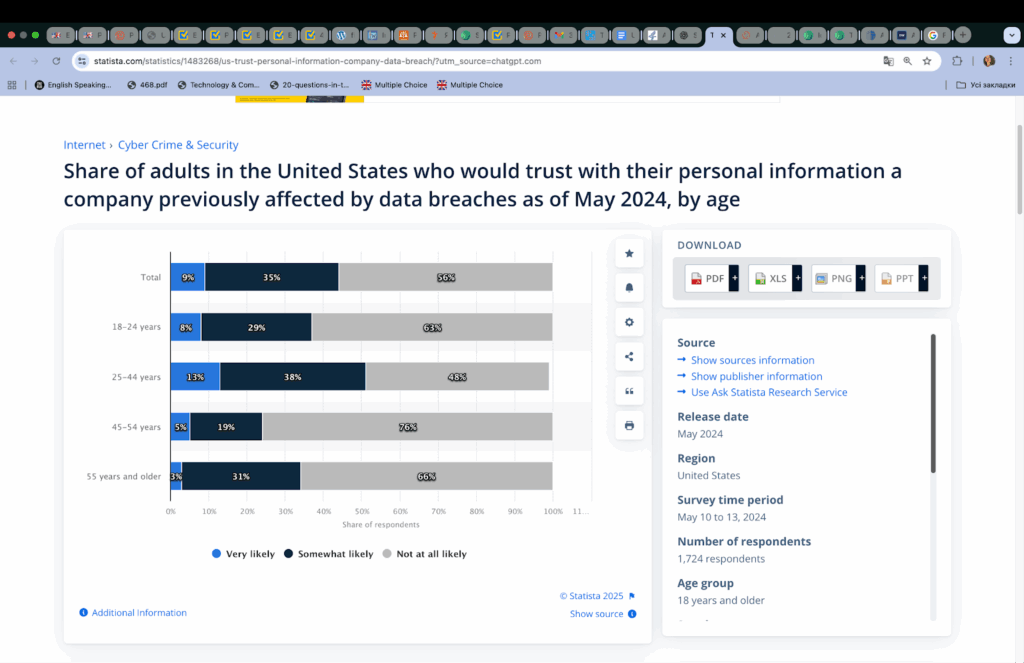
Trust is hard to earn and easy to lose. Once confidential information leaks, stakeholders hesitate to share documents, deals stall, and reputations take a hit. In the U.S., a 2024 Statista survey found that 56% of respondents wouldn’t trust a company again after a breach. It’s one of those risks where the impact lingers long after the incident itself.
4. Operational disruption
A breach doesn’t just affect finance or trust—it slows the whole business down. Systems can go offline, investigations take weeks, and resources get stretched thin. The Accellion file transfer appliance breach in 2020–2021 disrupted law firms, universities, and government agencies for weeks while data was patched and restored. Organizations that don’t invest in secure transfer methods end up paying in time and productivity.
5. Long-term reputational damage
Mishandled data can stick around in the market’s memory for years. It can make future deals harder, attract regulatory attention, and become an example others point to. The U.S. Office of Personnel Management breach, which exposed millions of federal employee records, is still cited as a benchmark failure in secure data handling.
If you invest in strong encryption, access controls, and clear workflow processes, you will protect data, safeguard your reputation, and keep business running smoothly. Organizations that adapt faster will always be ahead of those stuck relying on outdated methods.
💡 Additional resources: SharePoint vs virtual data room? How to choose the best solution?
Key features of a secure file transfer solution
The following solutions ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access, regulatory obligations are met, and the system can scale with organizational needs.
| Secure transfer protocol feature | Description | Importance |
| Encryption | 🔹 Protects data from interception 🔹 Uses AES-256 for file content and TLS 1.3 for connections 🔹 Encrypts data in transit and at rest 🔹 Ensures proper key management | Prevents data breaches and protects sensitive corporate, client, and partner information. |
| Authentication | 🔹 Confirms that only authorized users can access and securely transfer files 🔹 Implements multi-factor authentication 🔹 Can integrate with single sign-on | Reduces risk of unauthorized access and compromised credentials. |
| Compliance readiness | 🔹 Supports regulations such as HIPAA, SOX/GLBA, GDPR, and CCPA 🔹 Provides audit logs and access tracking 🔹 Enforces role-based permissions | Helps avoid costly fines, regulatory violations, and reputational damage. |
| Scalability | 🔹 Handles growth in users, file volumes, and transfer frequency 🔹 Supports large or batch transfers and multiple concurrent sessions 🔹 Integrates with existing IT systems without performance loss | Ensures the solution can grow with the business and support operational efficiency. |
| Monitoring and auditing | 🔹 Tracks all file transfers and detects unusual user activity 🔹 Offers real-time monitoring and automated alerts 🔹 Maintains detailed audit logs | Enables early threat detection and supports compliance. |
Together, these security features form the foundation of a secure file transfer service. Data transfer encryption keeps data unreadable to outsiders, authentication methods ensure only the right people gain access, and compliance features provide proof that obligations are being met. In addition, scalability makes the system usable across an organization. Finally, monitoring and auditing deliver visibility and accountability.
With these criteria in mind, the question becomes which methods meet them in practice.
Common secure file transfer methods
In this section, we examine the most common data exchange methods, their functionality, optimal applications, and their advantages and disadvantages.
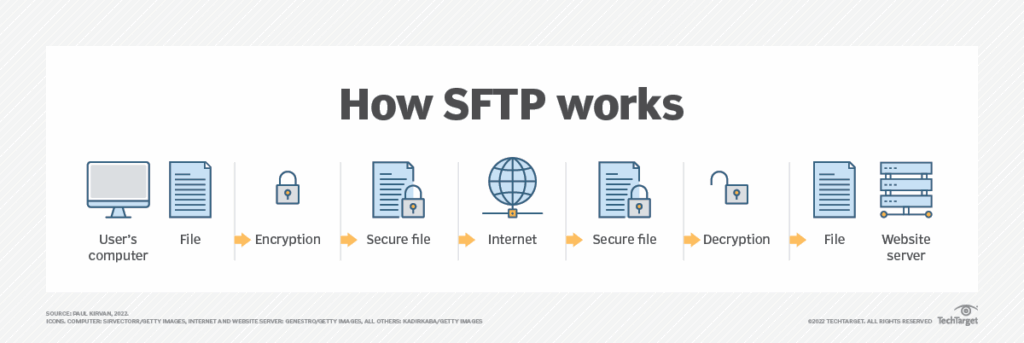
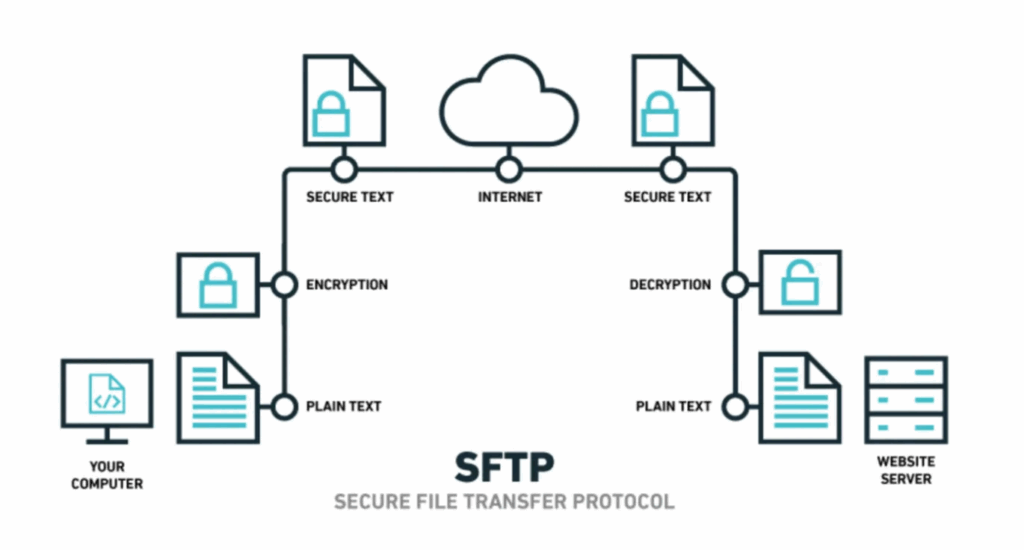
1. SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
SFTP is the choice for organizations that need structured, secure file movement. Built on SSH File Transfer Protocol, it encrypts commands, credentials, and file contents before they leave the system. It can resume interrupted transfers, manage directories, and automate workflows with SSH keys. Many companies combine SFTP with VPNs to add another layer of protection.
2. FTPS (File Transfer Protocol Secure)
This method builds on the familiar FTP protocol but adds encryption through Transport Layer Security or Secure Sockets Layer. It secures credentials and file data, often using certificates to verify users and servers. Connections can be explicitly encrypted after connecting or automatically through implicit mode. Organizations that adopt FTPS can leverage existing FTP infrastructure while meeting encryption standards. This approach keeps data secure without overhauling workflows.
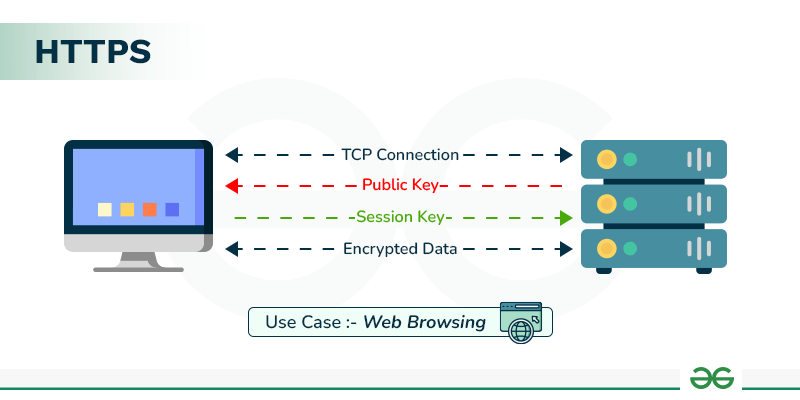
3. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
HTTPS is the secure connection used by most websites and online services that employees and clients access every day. It encrypts communications with TLS, protecting login credentials and files as they travel across the network. Files move through standard web ports, typically port 443, and can be accessed through browsers or APIs. Organizations often use HTTPS when ease of access and compatibility matter, integrating secure transfers directly into familiar workflows.
Source: GeeksforGeeks
4. MFT (Managed File Transfer)
Instead of focusing on a single protocol, this method centralizes transfers across the organization and supports SFTP, FTPS, and HTTPS (as well as AS2/AS3, WebDAV, email-based transfers, cloud storage connectors, and proprietary APIs). MFT adds encryption, authentication, workflow automation, monitoring, and compliance reporting. It provides visibility, control, and the ability to meet regulatory requirements.
Quick reference: Secure file transfer methods (In simple terms)
✔️SFTP – Moves files securely between computers. Encrypts files and login information. Can handle large files and automated transfers.
✔️FTPS – Adds encryption to standard file transfers. Protects files and credentials and verifies who is sending and receiving.
✔️HTTPS – Sends and receives files safely through a web browser. Uses secure connections that most people encounter every day.
✔️MFT – Centralizes secure file transfers across an organization. Automates transfers, tracks activity, and helps meet security rules.
Comparison of common secure file transfer methods
This table summarizes secure large file transfer methods, their regulatory compliance coverage, and the main advantages and limitations.
| Method | Compliance | ✅ | ✖️ |
| 1. SFTP | HIPAA GDPR SOX | 🔹 Encrypts all data and credentials 🔹 Supports automation and SSH keys 🔹 Reliable for large or repeated transfers 🔹 Can integrate with VPNs | 🔹 Requires technical expertise 🔹 SSH keys must be securely stored 🔹 Limited user-friendly interfaces 🔹 Compatibility issues across some software |
| 2. FTPS | HIPAA GDPR SOX | 🔹 Encrypts commands and data 🔹 Supports certificate-based authentication 🔹 Works with existing FTP infrastructure 🔹 Flexible explicit or implicit encryption modes | 🔹 Requires multiple ports for firewalls 🔹 More complex setup than SFTP 🔹 Potential compatibility issues with older clients 🔹 Less suitable for automation |
| 3. HTTPS | HIPAA GDPR CCPA | 🔹 Widely familiar and accessible 🔹 Encrypts data and credentials 🔹 Works through standard web ports 🔹 No specialized software required | 🔹 Limited automation capabilities 🔹 Less control over large or complex transfers 🔹 May not integrate with legacy file transfer systems 🔹 Less suitable for high-volume enterprise file-sharing |
| 4. MFT | HIPAA GDPR SOX CCPA | 🔹 Centralizes multiple secure protocols 🔹 Provides encryption, authentication, monitoring, and auditing 🔹 Scales across the organization 🔹 Helps meet regulatory requirements | 🔹 Can be expensive to implement 🔹 More complex setup than single-protocol solutions 🔹 May require training for non-technical internal users |
Choosing the right file transfer method is more than a technical decision. Every industry has its own regulations, and even small differences can have big consequences. To account for these nuances, we’ve created the following mapping to show which options best meet each sector’s compliance requirements.
➕Industry-to-compliance mapping for recommended secure data transfer methods
| Industry | Key regulation | Recommended transfer method(s) | Rationale |
| Healthcare | HIPAA, HITECH | SFTP, MFT | Encrypts PHI in transit; SFTP for point-to-point, MFT for enterprise-wide transfers with monitoring |
| Finance / Banking | SOX, GLBA | SFTP, FTPS, MFT | Secures financial data; FTPS for external partners; MFT for automated enterprise workflows |
| Legal / M&A | GDPR, SOX | SFTP, MFT | Enables secure data exchange and audit trails for due diligence or contracts |
| Government | FISMA, NIST, ITAR | SFTP, MFT | Encrypts sensitive data; MFT provides centralized monitoring |
| Retail / E-commerce | PCI-DSS | SFTP, FTPS | Secures credit card and payment data; FTPS useful for legacy integrations |
| General enterprise / SMBs | GDPR, CCPA | HTTPS, MFT | Secures client portals/cloud apps; MFT scales internal workflows, automation, and compliance reporting |
Generally, traditional file transfer methods are secure. At the same time, they can be fragmented and cumbersome. In particular, teams often have to manage multiple protocols, configure firewalls, monitor transfers separately, and ensure compliance across different systems. That can slow down workflows and increase the risk of errors.
Modern businesses need a solution that brings control, visibility, and secure collaboration tools together in one platform. In the next section, we explore this solution.
How VDRs ensure secure large file transfer
Virtual data rooms are easy-to-use, secure, centralized platforms that enable organizations to store, share, and manage sensitive files. The solution ensures file transfer compliance, visibility, and collaboration across internal teams and external partners.
Virtual data rooms provide the following tools for data protection and management:
1. Strong encryption
Virtual data rooms protect sensitive data at every step. Documents are encrypted in transit and at rest. High-grade TLS protocols and 256-bit AES keys keep sensitive information unreadable to users without permissions. Storing encryption keys separately from the business-critical data adds an extra layer of security.
2. User access controls
Administrators define who can view or edit each file, when they can do it, and from which locations or devices. Email verification, IP restrictions, and user- or group-level permissions ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information. Furthermore, permissions can be updated or revoked.
3. Audit trails
Every action in the data room, including opening, downloading, or modifying a file, is tracked down to the second. Heat maps provide visual insight into activity. Audit logs can integrate with security systems. This visibility helps organizations stay compliant and maintain oversight.
4. Built-in compliance
Organizations can select where their data is stored (Europe, Asia, Oceania, or the Americas) to meet regulatory requirements and maintain optimal performance. VDRs comply with AICPA, SOC, ISO, GDPR, and HIPAA. It reduces legal risk and helps teams demonstrate adherence to regulations.
5. User verification
Multi-factor authentication and email verification confirm that each user is authorized. Teams can trust that sensitive files are accessed only by the right people. These security mechanisms improve accountability and security.
6. Workflow automation
Notifications, document expirations, and approvals are automated. Teams can keep track of deadlines and file activity while minimizing mistakes. Using a data room checklist alongside these features helps ensure all necessary documents are uploaded and permissions are set correctly.
Why do companies choose virtual data rooms?
- Security with peace of mind. For a long time, the fear of leaks and breaches defined how companies handled sensitive information. Now, VDRs ensure data integrity and protection. This assurance allows leaders to focus on their mission and growth.
- Faster negotiations. Deals used to slow down when business partners and advisors had to move files across scattered systems. A single secure space changes that. Documents get reviewed faster, decisions come sooner, and projects don’t stall.
- Clarity and accountability. Businesses once struggled with a lack of visibility when files were shared. Today, real-time tracking shows exactly who accessed what and when, giving decision-makers the confidence to act decisively.
- Stronger collaboration. Internal teams and outside partners no longer juggle multiple platforms. With everyone working in the same secure environment, friction disappears and mistakes become far less likely.
- Time saved on routine work. Repetitive tasks like reminders, approvals, or document expiration used to take lots of time. Now, VDR automation handles the basics, freeing teams to concentrate on strategy and growth.
- Compliance built in. Passing audits and meeting regulatory demands has become part of daily operations. Compliant online data rooms allow businesses to avoid costly penalties, maintain credibility, and strengthen trust with stakeholders.
- Security as a driver of growth. Apart from protecting data with VDRs, dealmakers can open the door to global expansion, stronger partnerships, and confident scaling thanks to the trust, transparency, and efficiency these platforms bring to every transaction.
Clear breakdown of per-page, per-user, and flat-rate structures. Understand hidden costs before you commit.
View Pricing GuideExample case studies: Secure file transfer methods vs. virtual data rooms
Now, look at how secure file transfer methods and virtual data rooms work in practice.
Scenario: A mid-sized biotech company is preparing to partner with a global pharmaceutical firm. Sensitive research data, financial records, and legal agreements need to be shared securely across teams in different regions.
| Case | Secure file transfer | Virtual data room |
| How it works | The company uses SFTP and encrypted email to move files. Each team sets up access separately. Updates are sent through multiple channels. | All documents are uploaded into a VDR. Access is granted through roles and permissions, with audit trails, expiry dates, and automated alerts. |
| Experience | Security is maintained, but the process is fragmented. Team members spend time confirming versions, managing transfers, and resolving access issues. | Teams work in one environment. Everyone sees the latest version, access is clear, and audit logs run in the background without extra effort. |
| Result | Sensitive data remains protected, but collaboration slows. Deadlines stretch as teams juggle different systems. Compliance checks take additional time. | The deal moves forward faster. The biotech company impresses its partner with professionalism, passes compliance reviews smoothly, and secures the partnership on schedule. |
| Business impact | Security is achieved. Growth is delayed. | Security enables growth, making the company a stronger partner on the global stage. |
Final thoughts
The right file transfer approach can protect your business, keep operations running smoothly, and support collaboration at scale. At the same time, modern businesses gain advantages when they adopt secure, trackable systems or centralized platforms like virtual data rooms.
Companies that need a structured and point-to-point way to transfer data may find SFTP or FTPS sufficient. However, organizations transferring large files and managing multiple teams or complex compliance requirements often benefit from a managed file transfer solution or a VDR. The key is to match the method to your workflow, security needs, and regulatory obligations.
FAQ
1. Is email good for secure cloud file transfer?
Email isn’t inherently secure. Without encryption, sensitive files can be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties. For confidential data, organizations need encrypted, auditable methods like SFTP, FTPS, or VDRs.
2. What is the most secure file transfer protocol?
The most secure approach depends on your needs. Point-to-point transfers benefit from SFTP or FTPS, but for enterprise-wide visibility, compliance, and workflow automation, managed file transfer solutions or virtual data rooms offer the highest level of control and protection.
3. What’s the difference between SFTP and FTPS?
Both deliver encrypted file transfer. However, SFTP runs over Secure Shell (SSH) and combines commands and data into a single encrypted connection. FTPS, in turn, adds TLS/SSL encryption to traditional FTP. Also, SFTP often handles automation and large files more reliably, while FTPS can integrate with existing FTP infrastructure more easily.
Recommended for you


